Prominent retroclival venous plexus, normal anatomic variant
Images
CASE SUMMARY
A 56-year-old woman with a history of migraine headaches presented with one-month history of daily, right-sided, pulsating headaches, often associated with photophobia and vision changes in her right eye. She often woke up in the morning with these headaches and they tended to resolve spontaneously later in the day. She said she took sumatriptan sparingly, as she reported being averse to using this medication often, but triptans are generally helpful in resolving her headaches. She had no other relevant past medical or surgical history and her physical exam was benign. She was referred for MRI to evaluate for intracranial cause of headache.
IMAGING FINDINGS
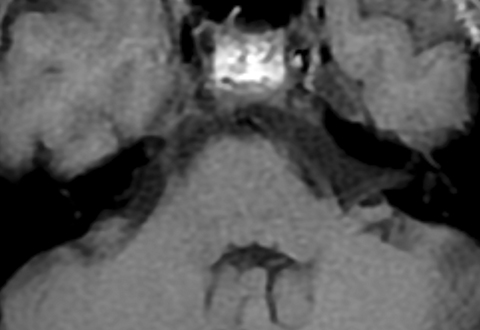
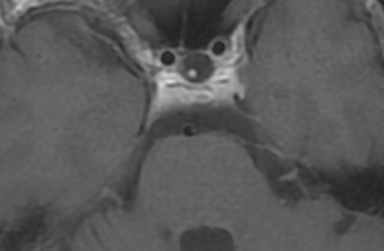
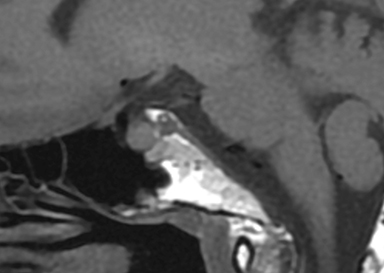
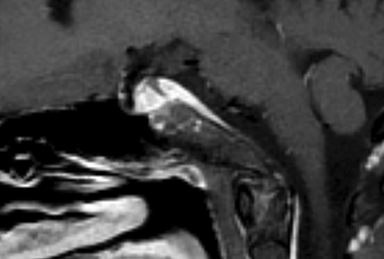
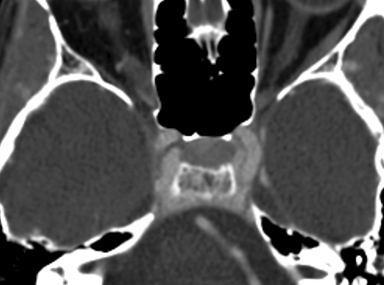
Axial MR imaging of the brain with and without contrast (Figures 1, 2) showed a soft-tissue prominence dorsal to the clivus, but did not show evidence of a mass within the clivus or mass effect on surrounding vasculature or brainstem. Clival T1-weighted signal intensity was within normal limits. Sagittal T1-weighted imaging (Figures 3, 4) demonstrated soft-tissue mass dorsal to the clivus with similar contrast enhancement pattern compared to nearby cervical vasculature. There was no involvement of the cavernous sinus. CT imaging of the sella turcica with contrast (Figure 5) showed enhancing soft-tissue mass dorsal to clivus with enhancement pattern consistent with surrounding skull base vasculature.
DIAGNOSIS
Prominent retroclival venous plexus, normal anatomic variant
DISCUSSION
The clivus is a midline, wedge-shaped segment of the central skull base that extends inferiorly to the foramen magnum and is bordered laterally by the petroclival fissures. Homogeneous hyperintensity of the clivus on T1-weighted imaging is a normal, age-related finding, found in one-third of patients in the third decade of life. As patients age, the proportion of patients demonstrating clival hyperintensity on T1-weighted images increases across decades and approaches 80-100% in the 8th and 9th decades of life.1,2 A hypodense clivus in an adult patient should raise concern for potential pathology.
The differential diagnosis for a clival mass can be divided into three major categories: disease originating from the clivus, disease originating from adjacent structures, and vascular pathology.3 Masses originating from the clivus include bony metastases, chordomas, chondrosarcomas and plasmacytomas. These masses generally cause mass effect of the surrounding structures, result in bony erosion, and appear hypo- to isointense or T1-weighted imaging.4 Masses originating outside the clivus include meningiomas, nasopharyngeal cancers, craniopharyngiomas, and pituitary macroadenomas.1,5
Finally, subdural or epidural hematoma is occasionally present in the retroclival region either from trauma secondary to shearing of the bridging veins of the basilar plexus, trauma from ligament disruption and fracture, coagulopathy, or can be spontaneous.6 Clinically, patients presenting with clival masses can vary significantly, ranging from a complete lack of symptoms to headaches, cranial nerve palsies, focal neurological deficits, and endocrinopathies.3,4,7 T1 and T2 signal intensity of the clivus, contrast-enhancement characteristics, along with evaluation for underlying bony involvement and mass effect help in differentiating these etiologies.1 In our case, there was no hyperdensity on the CT without contrast to suggest hemorrhage, no underlying bony involvement, mass effect, or associated soft tissue mass, and the smooth enhancement along the posterior aspect of the clivus followed enhancement of the vasculature. The constellation of these findings ruled against a diagnosis of clival mass and supported diagnosis of a prominent retroclival venous plexus.
The development of venous anatomy at the base of the skull is especially variable and includes the cavernous sinus, the superior petrosal sinus, the inferior petrosal sinus, and the basilar venous plexus.8,9 This case likely represents a prominent basilar venous plexus in the retroclival region, which is not commonly seen on CT or MR imaging, or possibly a prominent inferior petro-occipital vein, which has been described in the literature.10 It is unlikely that this anatomic variant was the cause of our patient’s headache. Radiologists should be aware of this variable venous anatomy and distinguish between vascular variants and clival masses.
CONCLUSION
The clivus is a component of the midline skull base that exhibits characteristic, age-related T1-weighted intensity characteristics and imaging abnormalities in the area can often suggest presence of clival masses. Identifying abnormal variants of venous drainage at the base of the brain is critical in surgical decision making, as a surgery in this area can be associated with severe blood loss. Recognizing abnormal variants and differentiating anatomic variants from clival pathology will allow physicians to reassure patients regarding prognosis and future management.
REFERENCES
- Kimura F, Kim KS, Friedman H, Russell EJ, Breit R. MR imaging of the normal and abnormal clivus AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990 Dec;155(6):1285-1291.
- Okada Y, Aoki S, Barkovich AJ, et al. Cranial bone marrow in children: assessment of normal development with MR imaging. Radiology. 1989 Apr;171(1):161-164.
- Neelakantan A, Rana AK. Benign and malignant diseases of the clivus. Clin Radiol. 2014 Dec;69(12):1295-1303.
- Erdem E, Angtuaco EC, Van Hemert R, et al. Comprehensive review of intracranial chordoma. Radiographics. 2003 Jul-Aug;23(4):995-1009.
- Appel JG, Bergsneider M, Vinters H. Acromegaly due to an ectopic pituitary adenoma in the clivus: Case report and review of literature. Pituitary. 2012 Dec;15 Suppl 1:S53-556.
- Narvid J, Amans MR, Cooke DL, et al. Spontaneous retroclival hematoma: A case series. J Neurosurg. 016 Mar;124(3):716-719.
- Rocque BG1, Herold KA, Salamat MS, et al. Symptomatic hyperprolactinemia from an ectopic pituitary adenoma located in the clivus. Endocr Pract. 2009 Mar;15(2):143-148.
- Kiliç T, Akakin A. Anatomy of cerebral veins and sinuses. Front Neurol Neurosci 2008;23:4-15.
- Tubbs RS, Hansasuta A, Loukas M, et al. The basilar venous plexus. Clin Anat. 2007 Oct;20(7):755-759.
- Tubbs RS, Watanabe K, Loukas M, et al. Anatomy of the inferior petro-occipital vein and its relation to the base of the skull: Application to surgical and endovascular procedures of the skull base. Clin Anat. 2014 Jul;27(5):698-701.
Citation
D N, J C, K S. Prominent retroclival venous plexus, normal anatomic variant. Appl Radiol. 2018;(7):42-44.
July 6, 2018