Radiological Case: Lateral ventricle epidermoid
Images
CASE SUMMARY
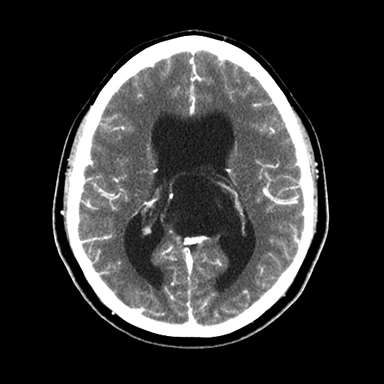
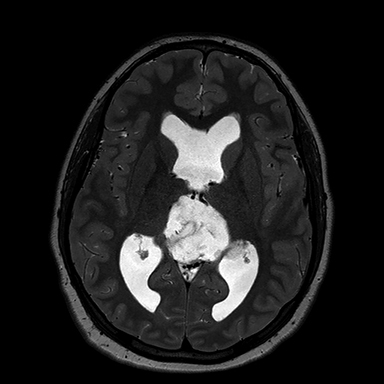
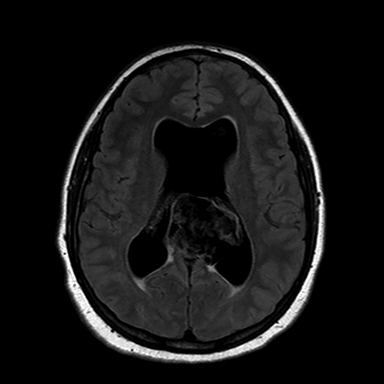
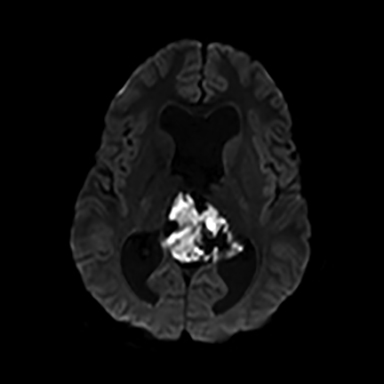
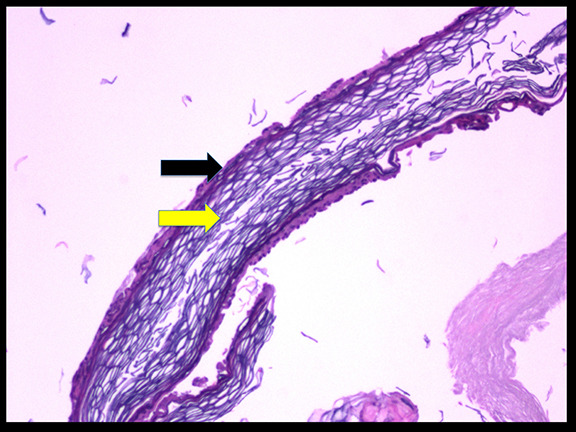
A 16-year-old male patient presented to an outside ER complaining of a headache. A noncontrast CT (NCCT) head revealed an intraventricular midline cystic mass. A contrast CT (CCT) head demonstrated minimal intralesional septal enhancement (Figure 1). The patient was then transferred to a tertiary pediatric hospital, where a brain MRI demonstrated a large, lobulated and septated T2 hyperintense mass within the posterior bodies of the lateral ventricles (Figure 2). There was intermediate signal intensity on T2 FLAIR within the interstices of the cyst (Figure 3) and positive diffusion restriction of the mass (Figure 4). The lateral and third ventricles were mildly dilated with periventricular T2 hyperintensity consistent with transependymal edema/resorption. A gross total resection was performed. Pathology confirmed this lesion to be an intraventricular epidermoid within the lateral ventricles (Figure 5).
IMAGING FINDINGS
The classic epidermoid imaging characteristics demonstrated by this case are diffusion positivity due to acellular debri. Epidermoids also have T1 hypointensity, T2 hyperintensity and intermediate heterogeneous FLAIR signal with thin, intralesional septal enhancement.
DIAGNOSIS
Lateral ventricle epidermoid. Differential diagnoses: arachnoid cyst, atypical choroid plexus papilloma, central neurocytoma or oligodendroglioma.
DISCUSSION
Epidermoids comprise approximately 0.2-1% of all intracranial tumors, usually presenting in the 4th or 5th decade.1 Most epidermoid cysts are congenital, although they may be acquired either postoperatively or from traumatic implantation. Of the total number of epidermoid occurences, there is < 1% incidence of an intraventricular epidermoid within the lateral ventricle.2,3 This entity has been previously reported, but only in an adult patient.4 Intraventricular epidermoid occurance in the pediatric population is an even rarer entity.1,5-7 In fact, no reported case of a pediatric lateral ventricle epidermoid was found in our literature search.6,8 Epidermoids are classically extra-axial, most frequently in the posterior fossa, and most commonly at the cerebellopontine angle. Secondary locations include the pineal region, the suprasellar cistern and the middle cranial fossa. If an epidermoid is within a ventricle the most common location is within the 4th ventricle. There is a 3rd-ventricle epidermoid reported in the pediatric population. However, this epidermoid may have spread from the interpeduncular cistern.9 The heterogeneity of epidermoids on FLAIR is presumed due to fibrous tissue and complex fluid within the interstices of the tumor10 Diffusion positivity is present in epidermoids but not arachnoid cysts.10,11
CONCLUSION
We have presented an epidermoid in the lateral ventricle in a pediatric patient. This case is the only known reported case in this population. In this example, there was mild hydrocephalus, possibly resulting from its mass effect. Epidermoids are of clinical significance for radiologists due to their classic appearance, which can differentiate them from other more aggressive tumors such as gliomas. Unless an intraventricular cystic lesion is an arachnoid cyst, it will require pathologic diagnosis. In this case, radiologists may confidently favor an epidermoid due to the complete diffusion restriction. A neoplasm may have patchy diffusion restriction, but this is usually not nearly as uniform as the restriction in an epidermoid. Epidermoids can demonstrate mass effect, but often less than expected for the size of the lesion. The intermediate FLAIR signal due to incomplete fluid restriction is also characteristic. Rarely, CSF flow signal could mimic this in an arachnoid cyst. Howevr an arachnoid cyst will never demonstrate diffusion restriction nor demonstrate enhancement and only rarely may have a small septation. Many neoplasms such as gliomas or metastasis will have primarily T2 hyperintensity. The two most notable exceptions to this rule are lymphoma and meningioma. The thin enhancement of intralesional septa is also more characteristic for epidermoids than a neoplasm. In summary, a lateral ventricle epidermoid is rare and this is the first known reported case in a pediatric patient. An epidermoid’s most characteristic imaging finding to differentiate from an arachnoid cysts is diffusion restriction.
REFERENCES
- Osborn AG, Preece MT. Intracranial cysts: Radiologic-pathologic correlation and imaging approach. Radiology. 2006;239(3):650-664.
- Koot RW, Jagtap AP, Akkerman EM, Den Heeten GJ, Majoie CB. Epidermoid of the lateral ventricle: Evaluation with diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor imaging. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.2003;105(4):270-273.
- Eekhof JL, Thomeer RT, Bots GT. Epidermoid tumor in the lateral ventricle. Surgical neurology. 1985;23(2):189-192.
- Ohata M, Inaba Y, Kuwabara T, Takahashi S. [The epidermoid tumor of the lateral cerebral ventricle; report of a case (author’s transl)]. No shinkei geka. Neurological surgery.1976;4(1):95-99.
- Barkovich AJ, Raybaud C. Pediatric neuroimaging. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012.
- Bhatoe HS, Mukherji JD, Dutta V. Epidermoid tumour of the lateral ventricle. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006;148(3):339-342; discussion 342.
- Dastur DK, Lalitha VS. Pathological analysis of intracranial space-occupying lesions in 1000 cases including children. 2. Incidence, types and unusual cases of glioma. Journal of the neurological sciences. 1969;8(1):143-170.
- Franko A, Holjar-Erlić I, Miletić D. Lateral ventricle epidermoid. Radiology and Oncology. 2008;42(2).
- Behari S, Jaiswal S, Nair P, Garg P, Jaiswal AK. Tumors of the posterior third ventricular region in pediatric patients: The Indian perspective and a review of literature. Journal of pediatric neurosciences. 2011;6(Suppl 1):S56-71.
- Tampieri D, Melanson D, Ethier R. MR imaging of epidermoid cysts. AJNR. Am J Neuroradiol. 1989;10(2):351-356.
- Jolapara M, Patro SN, Kesavadas C, et al. Can diffusion tensor metrics help in preoperative grading of diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas? A retrospective study of 36 cases. Neuroradiology. 2011;53(1):63-68.
Citation
AM M, J E, D S, P D, JH M, PD A.Radiological Case: Lateral ventricle epidermoid. Appl Radiol. 2015; (12):16-18.
December 17, 2015