Technology and Industry: RSNA 2005 review: Part 1


More than 26,600 imaging professionals were among the more than 61,500 attendees at the 91st Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA 2005), held November 27 to December 2, 2005 in Chicago, IL.
Attendees could chose from more than 300 refresher courses, 150 infoRAD exhibits, 7 hands-on computer workshops, and more than 1100 educational exhibits, and could meet with more than 680 technical exhibitors who filled nearly 470,000 square feet of the McCormick Place Convention Center.
Siemens Medical Solutions features MR technologies
Siemens Medical Solutions (Malvern, PA) displayed its full line of imaging products at RSNA 2005, highlighting recent enhancements to the company's magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and radiography technologies as well as previews of several works-in-progress.
In the field of MR imaging, Siemens introduced several advanced applications that draw on the combination of its Tim (Total imaging matrix) and syngo applications. Among the featured applications were syngo SPACE and syngo SWI. The syngo SPACE was designed to provide fast, accurate 3-dimensional (3D) contrast imaging that can replace multiple 2-dimensional (2D) acquisitions in certain anatomic areas, such as the complex spine, head, inner ear, abdomen, and pelvis. With the combination of SPACE and Tim's Parallel Imaging capabilities, the company notes, users can identify small plaques with higher confidence and can survey the brain with isotropic resolution in <5 minutes.
The susceptibility-weighted imaging technique, syngo SWI, was developed to show blood products and venous structures with greater clarity quickly, particularly for depiction of bleeding in stroke and brain trauma patients, visualization of contusions and shearing injuries, and identification of minute intracranial vascular malformations.
The company also showcased its Tim Breast Suite for MR imaging of the breast. This solution includes dedicated protocols in various orientations, providing image assessment in any plane, and DynaCAD, a set of Siemens-optimized computer-aided detection (CAD) tools designed for use in breast MR imaging.
Siemens also featured the MAGNETOM Trio, a 3T whole-body MR system with Tim (Figure 1), and the MAGNETOM Espree, an open-bore 1.5T system, also equipped with Tim. The proprietary Tim technology is a seamless, whole-body surface coil design that combines up to 102 integrated coil elements with up to 32 radiofrequency channels. According to Siemens, it enables flexible-coil combinations that can encompass a variety of imaging needs for local high-resolution imaging or large anatomical coverage of up to 205 cm (6′9″) without patient repositioning or coil changes.
The company also previewed the capabilities of syngo Expert-i as a work-in-progress. Syngo Expert-i gives physicians the ability to remotely interact from virtually anywhere during an MR examination. While the patient is being scanned, the entire patient set-up, imaging data, and all sequences can be viewed in real-time, via a networked personal computer. Siemens conducted 2 real-time live remote scans each day from the University of California, Los Angeles and Northwestern University, Chicago, IL.
"As an innovation leader in MR, Siemens is constantly enhancing its portfolio of clinical applications, helping the clinician achieve faster, more accurate diagnostic workflow," said Nancy Gillen, Vice President, MRI Division, Siemens Medical Solutions. "Tim-powered applications have brought medical imaging to the next level by allowing doctors to detect and diagnose disease states earlier, offer more treatment options, and increase workflow and efficiency."
Philips focuses on connectivity
Philips Medical Systems (Bothell, WA) designed its RSNA 2005 display around the concept of connectivity. Using a fictional patient named "Ana," Philips showed attendees how a variety of the company's technologies can work together to improve patient care. The featured systems included the company's Smart Exam, a new MR workflow system; the Brilliance Workspace Portal and Halo computed tomography (CT) products, designed to address patient throughput and comfort though new data management, access, and product design; and the company's new PET/CT Viewer that is available on the Extended Brilliance Workspace.
"Philips is keenly aware that in order to contribute to the increased efficiency, safety, and effectiveness of the healthcare system, we need to design advanced new medical technologies that are fully integrated with their surroundings," said Brent Shafer, Philips' Executive Vice President and CEO, North America. "Our technology portfolio clearly illustrates how the advanced new radiology solutions we are introducing this year, and have in past years, all integrate into the patient care cycle, allowing clinicians to focus on their patients."
For the first time at RSNA, Philips also showed the new DigitalDiagnost Compact, a step-in solution for direct digital radiography. Designed for all general radiography applications at moderate throughput rates, the system includes a 17 ×17-inch flat detector mounted on a fixed, multipurpose stand with a tilting and swiveling arm, a trolley with a 4-way floating table top, and a ceiling-suspended tube carrier.
In the field of radiography, Philips introduced its new fully motorized, mobile X-ray system, Practix Convenio (Figure 2). This system combines motorized maneuverability and a battery capable of a full day of applications before it must be recharged. Designed for use in the intensive care and emergency departments, the system includes a swiveling column, a telescopic tube arm, and motor-assisted fine positioning from the tube head as well as 36 Anatomically Programmed Radiography settings and "hot key" functionality for commonly used customer settings.
Finally, also as works-in-progress, Philips previewed 2 new CT technologies. The first, the Simultaneous Multi Energy detector, is currently undergoing clinical trials in Israel. This new CT detector is made up of layers designed to simultaneously detect both low-energy (soft) and high-energy (hard) X-rays. The company believes that simultaneous imaging of both soft and hard radiation will improve tissue characterization without requiring a second beam of radiation, thereby avoiding the problems of time lag, registration artifacts, and increased radiation dose. The second innovation is a full-coverage detector platform based on Nano-Panel technology that will image an entire organ, such as the heart or head, in a single rotation.
Hologic previews works-in-progress
Hologic, Inc. (Bedford, MA) unveiled 2 significant works-in-progress at RSNA this year: Breast tomosynthesis with a selenium-based detector and 3D image reconstruction for dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
Following 2 years of diagnostic and screening clinical trials, Hologic presented its latest breast tomosynthesis images (Figure 3). The company noted that it expects that the ongoing trials will find improved sensitivity and specificity with digital breast tomosynthesis compared with 2D digital mammography.
The company also announced the formation of a strategic research collaboration with Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, for the development of tomographic 3D image reconstruction of the hip utilizing the company's Discovery line of bone densitometers and presented such images as works-in-progress.
Hologic's Discovery technology uses its patented rotating C-arm to acquire multiple views of the femur at different angles. Researchers at Johns Hopkins then use this low-dose acquisition to construct a 3D volumetric model of the femur, which the company believes will allow for a more accurate assessment of the complex femur structure.
"Clinicians have long sought the next generation of osteoporosis assessment tools to better predict femur fracture risk," said Brad Herrington, Vice President of skeletal health imaging. "Virtually all imaging modalities have turned to 3D. We believe that a low-dose tomographic assessment of bone density and geometry may provide the ultimate clinical tool to discern bone structure and strength. Our hope is that tomographic 3D analysis will ultimately be available on all Discovery systems with rotational C-arm capability."
The company is seeking researchers to assist with the clinical validation of this new imaging feature.
GE Healthcare focuses on early detection
GE Healthcare's (Chalfont St. Giles, UK) display at RSNA 2005 featured technologies designed to "enable an 'early health' model of care in the future, focused on earlier diagnosis, presymptomatic disease detection, and disease prevention."
"We are providing transformational medical technologies that are shaping a new age of patient care," said Joe Hogan, company President and CEO. "GE's expertise in medical imaging and information technologies, medical diagnostics, and drug discovery is helping radiologists around the world reimagine new ways to predict, diagnose, inform, and treat disease earlier, so their patients can live their lives to the fullest."
GE Healthcare displayed a range of products and services, including the company's volumetric CT scanner, the LightSpeed VCT, and a new bone mineral density system, the Lunar iDXA.
The company noted that LightSpeed VCT is the fastest-selling product in GE Healthcare's history: 5 months after announcing the 100th worldwide installation, the company announced the 500th worldwide installation at RSNA.
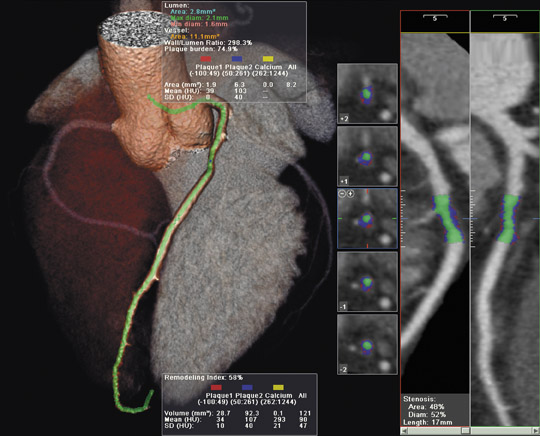
The LightSpeed VCT (which can create 64 submillimeter images, totaling 40 mm of anatomical coverage, in a single rotation) features several cardiovascular applications (Figure 4). The 5-Beat Cardiac application was designed to allow physicians to scan the human heart in as few as
5 beats. The Triple RuleOut feature was developed to help clinicians rule out (or diagnose) aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism, and coronary artery disease with a single scan. The Stroke WorkUp feature provides the ability to dynamically acquire both anatomy and perfusion/ blood flow to the brain in one scan.
The company also introduced its latest bone mineral density system, the Lunar iDXA, at RSNA 2005 (Figure 5). Approved for marketing in October 2005, this system can handle patients weighing up to 400 lbs and allows clinicians to simultaneously assess body composition and ascertain fat distribution while the patient is undergoing bone mineral density testing. It can also determine regional body fat composition, which is an important indicator of risk for diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
"The new iDXA provides both excellent image quality and precise bone density measurements, allowing clinicians to better assess bone mineral density, bone structure, and, ultimately, bone strength," said Ken Faulkner, chief scientist for GE Healthcare's Lunar business. As a result, clinicians can monitor a patient's progress and response to therapy earlier in the treatment process, by tracking changes in bone health that had previously been too minor to detect.
Medweb introduces RIS and Web PACS products
Medweb (San Francisco, CA) unveiled a new radiology information system (RIS), the Medweb Dashboard, at RSNA 2005.
Dashboard was designed to allow single or multisite radiology groups to share workloads between multiple picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) and hospital information systems (HIS) [or RIS], regardless of vendor. The system provides what the company calls a "virtual reading room" that automatically loads, assigns, and reassigns cases to radiologists based on workload, rather than location. It also allows the user to route exams based on customizable rules based on a radiologist's state licensure, hospital privileges, subspecialty, or real-time workload balancing.
This system handles images, dictation, transcription, and reporting. Voice recognition and billing capabilities are available as options. It also tracks statistics and turnaround times, automates reassignment of studies within a designated time frame, and prioritizes stat exams as part of the basic workflow. A dictation and viewing interface automatically routes and reinserts the signed reports back to the originating PACS, RIS, fax, or printer as an HL7 or DICOM electronic message, fax, printout, or e-mail, according to the preferences of the client facility. It also includes a private, encrypted instant messaging system for collaboration between physicians.
The company also introduced its new Medweb Advanced 3D Web PACS at this year's meeting. This system allows users on a standard personal computer to perform advanced 3D templating and auto segmentation of image data from multislice CT scanners.
Designed for use in the evaluation of studies originating on 16- and 32-slice CT scanners, Medweb Advanced 3D Web PACS allows the distribution of information in a 3D volume that the company notes is easy to display and navigate. It allows the user to perform isolation, sculpting, zoom-in, and 360˚ image rotation, as well as maximum-intensity projection (MIP), multiplanar reformatting (MPR), various measurements, and 3D cursor functions alongside conventional 2D image windows (Figure 6). The auto segmentation tools isolate bone, blood vessels, and other organs, using either simple template buttons or customizable settings without the need for a dedicated 3D workstation.
Medweb Advanced 3D Web PACS can be integrated into a conventional PACS infrastructure, can act as a standalone PACS, or can function as a modality PACS system for the increased imaging demands created by the latest CT technology.
