Ultrasound and MR Imaging Aid in Diagnosing Placental Accreta Spectrum
 Accurate prenatal diagnosis of severe placental accreta spectrum (PAS) disorder by imaging could help guide maternal counseling and selection between hysterectomy and uterine-preserving surgery, according to an open access article in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
Accurate prenatal diagnosis of severe placental accreta spectrum (PAS) disorder by imaging could help guide maternal counseling and selection between hysterectomy and uterine-preserving surgery, according to an open access article in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
“The findings suggest strong performance of placental bulge in diagnosing severe PAS on both ultrasound and MRI, with potentially relatively stronger performance on MRI,” wrote corresponding author Manjiri Dighe from the department of radiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “Nonetheless, interobserver agreement remains suboptimal on both modalities.”
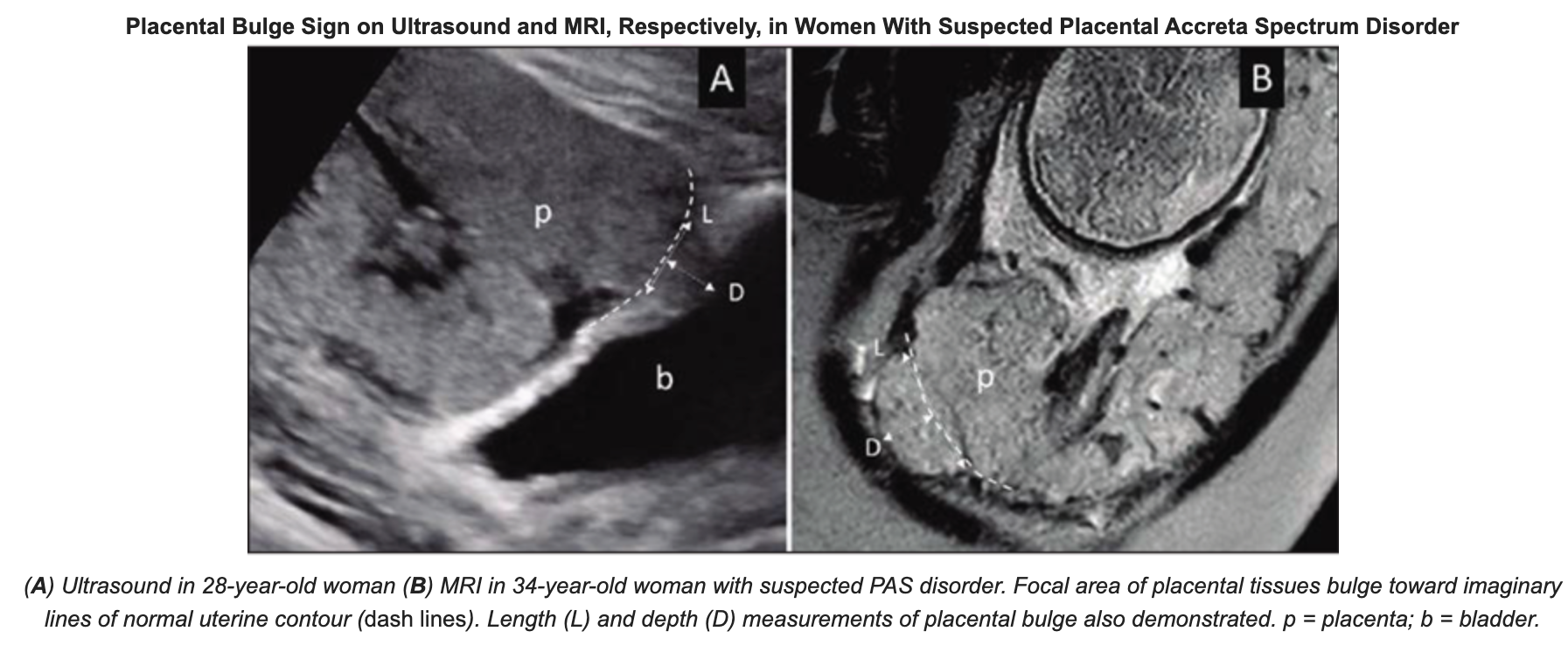
On ultrasound and MRI alike, the placental bulge sign represents deeper venous invasion in PAS—the focal area of myometrial-placental bulging beyond the normal uterine contour. Dighe and colleagues’ retrospective study included 62 pregnant women (mean age, 33.2 years) with clinically suspected PAS who underwent both ultrasound and MRI. Blinded to final diagnoses, two maternal-fetal medicine specialists for ultrasound and three abdominal radiologists for MRI independently reviewed images for their respective modality. Using intraoperative and pathologic findings, alongside International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics classification, patients were separated into those with and without severe PAS.
“In diagnosing severe PAS,” Dighe et al. noted, “placental bulge sign achieved on ultrasound an accuracy of 85.5%, sensitivity of 91.7%, and specificity of 76.9%, and on MRI an accuracy of 90.3%, sensitivity of 94.4%, and specificity of 84.6%.”
Ultimately, placental bulge was an independent predictor of severe PAS on ultrasound (odds ratio=8.94) and MRI (odds ratio=45.67). The authors concluded that placental bulge sign on either prenatal ultrasound or MRI may help diagnose severe PAS warranting hysterectomy rather than conservative management.